“The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value.” -Don Tapscott
What is Blockchain?
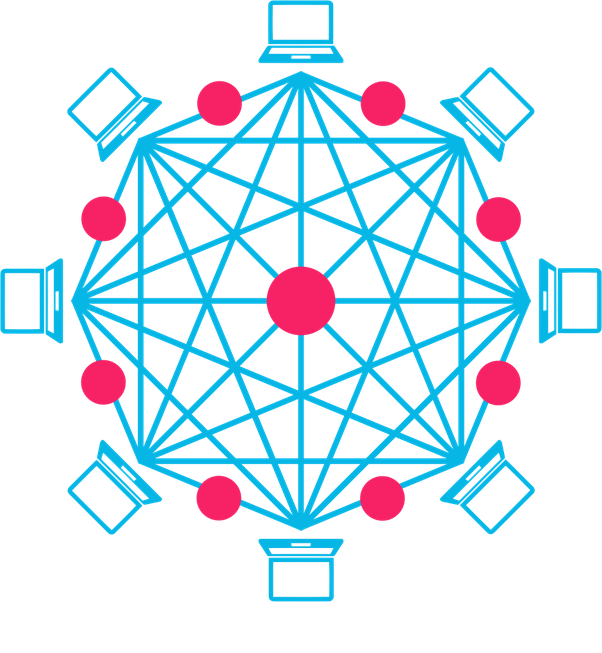
A Blockchain is a global online database which anyone anywhere with an internet connection can use. Because it exists on the internet, it is “decentralized”, meaning the blockchain ledger is shared among all computers around the world, not in one central location. the blockchain cannot:
- Be controlled by any single entity.
- Has no single point of failure.
Why Blockchain Introduced? What is the need behind?
When it comes to transacting money or anything of value, people and businesses have relied heavily on intermediaries like banks and governments to ensure trust and certainty. Middlemen perform a range of important tasks that help build trust into the transactional process like authentication & record keeping.
To establish trust between ourselves, we depend on individual third-parties. what is the problem depending on them?
- What if that register in which the transaction was logged gets burnt in a fire?
- What if, by mistake/ by purpose, your account manager had written $50 instead of $100?
- What if that centralized person/organization got corrupted, intentionally or unintentionally?
Think about it for a second, what does transferring money means? Just an entry in the register. The better question would then be:
Could there be a system where we can still transfer money without needing the bank?
Is there a way to maintain the register among ourselves instead of someone else doing it for us?

Yes, It’s a Blockchain!!!
Currently, most people use a trusted middleman such as a bank to make a transaction. But blockchain allows consumers and suppliers to connect directly, removing the need for a third party.
How does a blockchain work?
The Blockchain is based on distributed ledger technology, which records data (transactions, files, or information) across a peer-to-peer network. These data is known as ‘Blocks’ that use cryptographic validation to link themselves together. Every participant can see the data/block and verify (or reject) it using consensus algorithms. Approved data is entered into the ledger as a collection of “blocks”, stored in a chronological “chain”, and secured through cryptography.
Now the questions are:
- How does this distributed ledger work?
- Who kept all the records and maintain Blocks?
- How the Verification takes place?
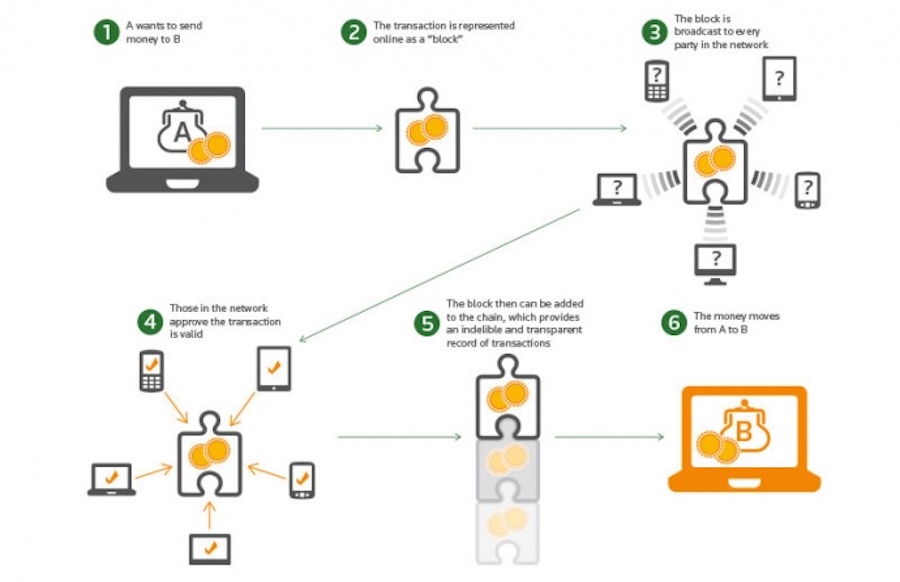
Consider N number of individuals want to give up on banks or any third-party. Upon mutual agreement, they have details of each other’s accounts all the time — without knowing the other’s identity.
Everyone in the network sits with a blank notebook and a pen in their hands. Everyone is ready to write any transaction that occurs within the system.
Whenever they want to make a transaction, they announce it to everyone else. As soon as a person listens to the announcement, he/she writes it on his/her notebook we can call it as a ledger.
# A distributed ledger has a network of replicated databases, synchronized via the internet and visible to anyone within the network.
# Blockchain networks can be private with restricted membership similar to an intranet, or public, like the Internet, accessible to any person in the world.
# When a digital transaction is carried out, it is grouped together in a cryptographically protected block with other transactions that have occurred in the last 10 minutes and sent out to the entire network.
# Miners (members in the network with high levels of computing power) then compete to validate the transactions by solving complex coded problems.
Then why does everyone spend resources doing the calculation when they know that someone else will calculate?
Great question 🙂
This is where the incentives come in the picture !!!
Everyone who is the part of the Blockchain is eligible for rewards. The first one to calculate the sealing number gets rewarded with free money for his efforts (i.e. expended CPU power and electricity).
The first miner to solve the problems and validate the block receives a reward. (In the Bitcoin Blockchain network, for example, a miner would receive Bitcoins).
The validated block of transactions is then time stamped and added to a chain in a linear, chronological order. New blocks of validated transactions are linked to older blocks, making a chain of blocks that show every transaction made in the history of that blockchain.
The entire chain is continually updated so that every ledger in the network is the same, giving each member the ability to prove who owns what at any given time.
Blockchain takes transactions, bundles them in blocks and chains them together using hashes created by the end user’s software. The information is sent out on the peer-to-peer architecture, where it is processed.
When changes are made to the information or ledger, those changes are recorded across the blockchain, often within seconds. In this way, the information on the blockchain is not only shared but also continually reconciled as changes to the data are made.
Cryptography protects all the records. Moreover, each block has a timestamp and a link to the prior block, with transactions recorded chronologically and, thus, forming an immutable chain.
Blockchain’s decentralized, open & cryptographic nature allows people to trust each other and transact peer to peer, making the need for intermediaries obsolete. This also brings unprecedented security benefits. Hacking attacks that commonly impact large centralized intermediaries like banks would be virtually impossible to pull off on the blockchain.
Explore More: Working of Blockchains and Bitcoin.
Bitcoin and Blockchain
The blockchain is seen as the main technological innovation of Bitcoin or in other words, Blockchain’s very first and most famous application is Bitcoin, a peer-to-peer digital currency for the modern, digital age. Bitcoin is created and held on Bitcoin’s blockchain. Unlike traditional money, you can send Bitcoin money to anyone and anywhere without seeking permission from banks or governments.
Although commonly associated with Bitcoin, blockchain technology has many other applications. The Blockchain is to Bitcoin, what the internet is to email. A big electronic system, on top of which you can build applications. Currency is just one.
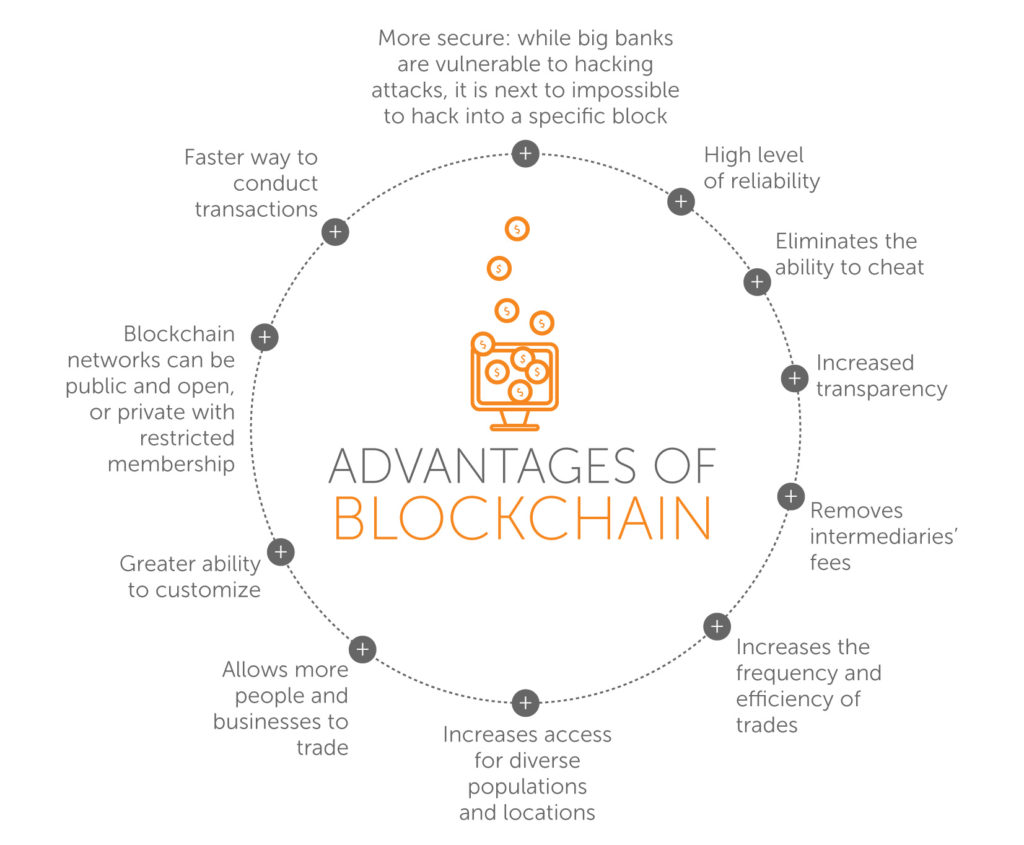
Experts cite several key benefits to Blockchain:
- Security is considered one of the major advantages of this technology. Also, the records are public, verifiable and almost impossible to corrupt because the information held on the blockchain is a shared and continually reconciled database hosted by thousands, even millions, of computers.
- Blockchain also has no single point of failure. Additionally, blockchain can reduce costs while increasing speed and efficiency because it removes intermediaries from transactions.
On the other hand, experts say blockchain also has potential drawbacks, risks, and challenges:
- There are questions about whether blockchain has enough safeguards to prevent problems and adequate governance to take responsibility and address any problems that arise.
- There are questions about whether organizations are capable or willing to invest in the infrastructure required to support widespread use of blockchain.
The technology likely to have the greatest impact on the next few decades has arrived. And it’s not social media. It’s not big data. It’s not robotics. It’s not even AI. You’ll be surprised to learn that it’s the underlying technology of digital currencies like Bitcoin. It’s called the blockchain
Blockchain has applications that go way beyond obvious things like digital currencies and money transfers. From electronic voting, smart contracts & digitally recorded property assets to patient health records management and proof of ownership for digital content.
Blockchain will profoundly disrupt hundreds of industries that rely on intermediaries, including banking, finance, academia, real estate, insurance, legal, health care and the public sector — amongst many others.




Pingback: Blockchain Technology: Everything You Need to Know – ARreverie Technology - Secure Signal NYC